Kanban Methodology
Kanban is the most mainstream lithe system after Scrum for programming advancement. It gives the constant and straightforwardness of work. In Kanban load up, all the assignments are noticeable that permits the colleagues to see the condition of each undertaking whenever.
Characteristics of Kanban methodology:
- Adaptability
- In Kanban philosophy, a group focusses on the work that is 'in progress' state. When the group finished its assignment, at that point it pulls the following first errand of the item build-up. An item proprietor reprioritizes the undertakings or made changes in an item accumulation outside the group, so this won't disturb or sway the group. An item proprietor keeps the most significant undertaking on the highest point of the item accumulation, so the improvement group guarantees that they will deliver the most important yield. In Kanban, we don't have to do the fixed-length emphasis as we did in the scrum.
- Limit time cycles
- The process duration is the measure of time taken by the work to go from the second it begins to the second it gets dispatched to the clients. A covering range of abilities can limit the process duration. In this, designers compose the code as well as test the code at whatever point required. This sort of sharing aptitudes implies the colleagues can take the heterogeneous work which upgrades the process duration.
- Visual measurements
- Visual measurements is a method of improving group productivity and group viability. A visual measurement is appeared through graphs, and colleagues can see the information in outlines, and can recognize the issues emerges in their procedure. The principle objective of the visual measurement is to decrease the measure of time taken by the issues to travel through the whole procedure.
- There are two kinds of graphs utilized by the kanban group:
- Control graphs: It shows the process duration taken by each issue.
- Aggregate stream charts: It shows the quantity of issues present in each state.
- Nonstop conveyance
- The primary point of ceaseless conveyance to convey the item with generally safe quickly. The progress from the spry techniques to ceaseless conveyance move the two-three weeks run to the Kanban philosophy. Both Kanban philosophy and constant conveyance supplement each other by conveying the item to the clients quicker. Programming advancement groups are utilized to create, test, and survey the new highlights in a persistent way. Hence, we can say that Kanban is a constant stream approach.
Kanban Board
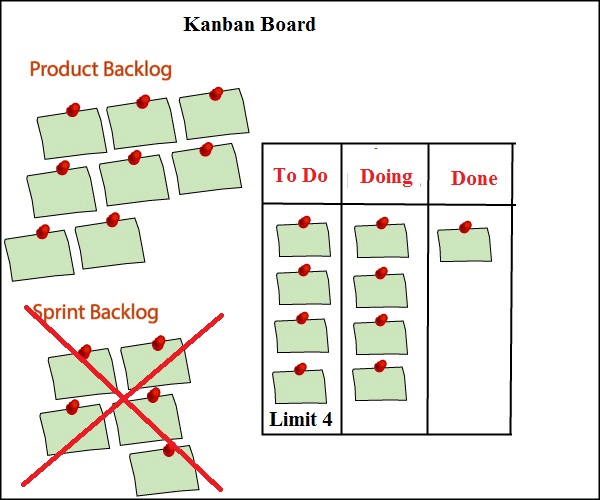
Kanban board is an apparatus used to envision the work and breaking point work-in-progress.
As in scrum, we are taking a few exercises from an item overabundance and including a run build-up. In any case, in Kanban, we don't have run, so run accumulation action won't be performed. This is the fundamental distinction among scrum and Kanban that scrum contains run excess while kanban doesn't contain the run accumulation.
Kanban board consists of three states:
- To Do
- Doing
- Done
At the point when the venture is begun, at that point we put all the exercises from the item build-up to the 'To Do' state. At the point when the colleague begins dealing with a movement, at that point that action is placed in a 'Doing' state, and when the action is put, at that point it is put in a 'Done' state.
From the Kanban board, one can become more acquainted with which exercises have been done and which exercises they have to create.
One of the most significant highlights of the Kanban board is a Limit choice. In the above figure, we have eight assignments in an item excess and breaking point set is 4. At once, it will take just four assignments in a 'To Do' state, and on the off chance that any of the undertakings arrive in a 'Doing' state, at that point one more errand from the item build-up will be put in a 'To Do' state. Along these lines, we can set the cutoff relying upon the accessibility of the assets.









